(Just Life / Shutterstock.com)
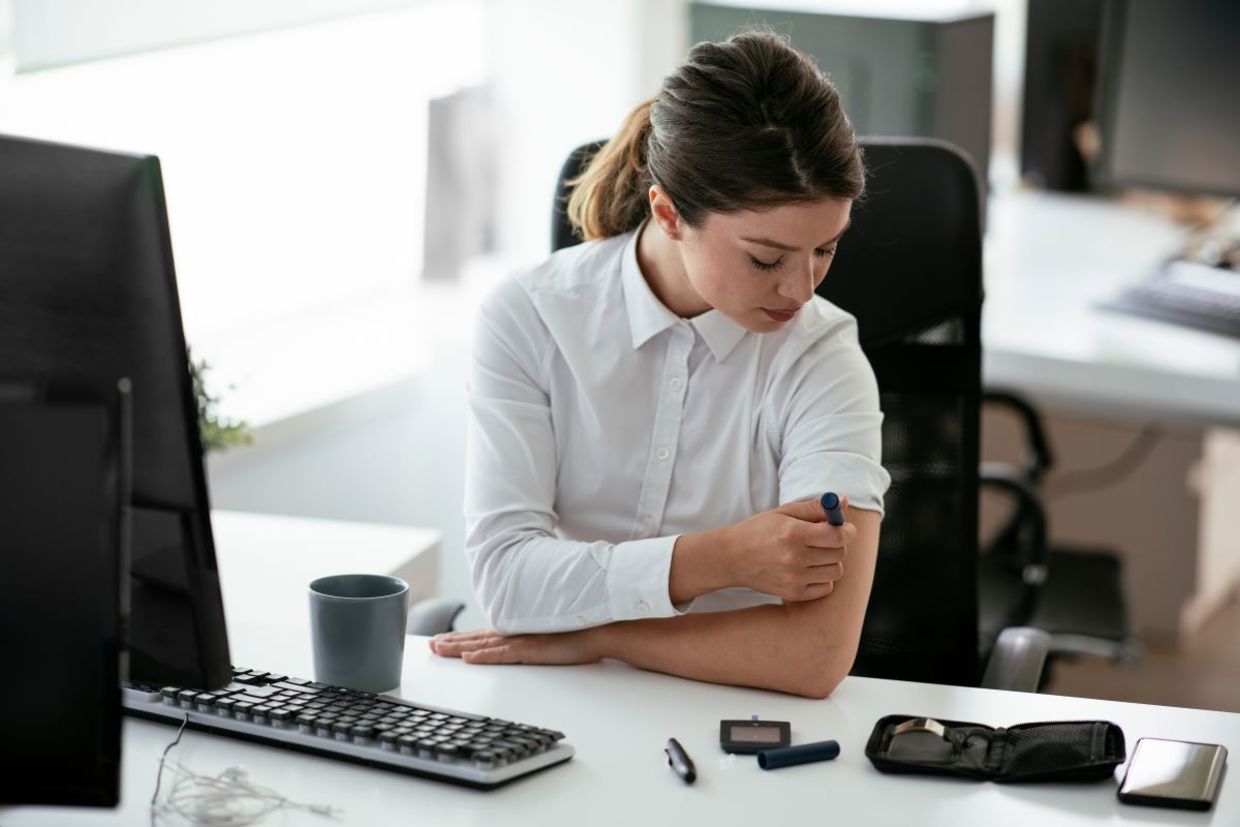
The discovery of synthetic insulin is one of the most important medical advances of the past century. It has saved the lives of countless millions of people. Now, scientists have begun to develop a new type of insulin that remains in the body for a week, making the numerous daily insulin injections that Type 1 diabetes patients are so familiar with a thing of the past.
Up to 10 insulin injections a day
Type 1 diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas cannot produce, or can only produce a little of the hormone insulin. Insulin is what allows the body to process glucose, which is vital for cells to produce energy.
Once, Type 1 diabetes was an incredibly dangerous disease, The Guardian reports. Now, with the advent of synthetic insulin, while not a walk in the park, it is no longer as life-threatening. What it is, however, is very difficult withType 1 diabetes patients having to inject themselves with insulin up to 10 times a day. The constant fluctuations in blood sugar could cause both short-term and long term health issues.
Luckily, researchers have discovered a way to create “smart insulin”: an insulin that lies dormant in the body and reacts to changes in blood sugar levels as they happen. It remains effective for a week. The study was recently published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“Glucose-responsive – so-called smart – insulins are regarded as the holy grail of insulin as they would come as close to a cure for type 1 diabetes as any drug therapy could,” Dr Tim Heise, vice-chair of the novel insulins scientific advisory panel for the Type 1 Diabetes Grand Challenge, told The Guardian.
Mice and mini pigs
So how does it work? According to New Atlas, the new type of injected insulin – which has been tested on mice and mini pigs, but not yet humans – forms a pea sized depot under the skin allowing for its slow release. When the researchers injected glucose into the subjects, the insulin immediately reacted to lower blood glucose levels, and when the subject’s blood glucose levels were back to normal it sent out a signal to reduce the rate of insulin release.
“Current study in the mini pig model indicates that this new formulation has long-lasting and glucose-responsive insulin release properties,” Zhen Gu, the corresponding author, told New Atlas. “It could maintain normal blood sugar levels in 30 kg (66 lb) minipig model for over one week with a single dose, without symptoms of hypoglycemia."
The combined effects of having an insulin that can respond in real-time to fluctuating blood sugar levels, and the fact that it only has to be administered once a week, could truly be life-changing for so many people with diabetes. Though there is still a long way to go before smart insulin hits the market, it is an incredible sign of hope.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE:
Synthetic Platelets are a Major Medical Game Changer
World's First Successful Maglev Titanium Heart Transplant
Discover the Future of Healing with Innovative Bone Replacement Technology