(YURII MASLAK / Shutterstock.com)
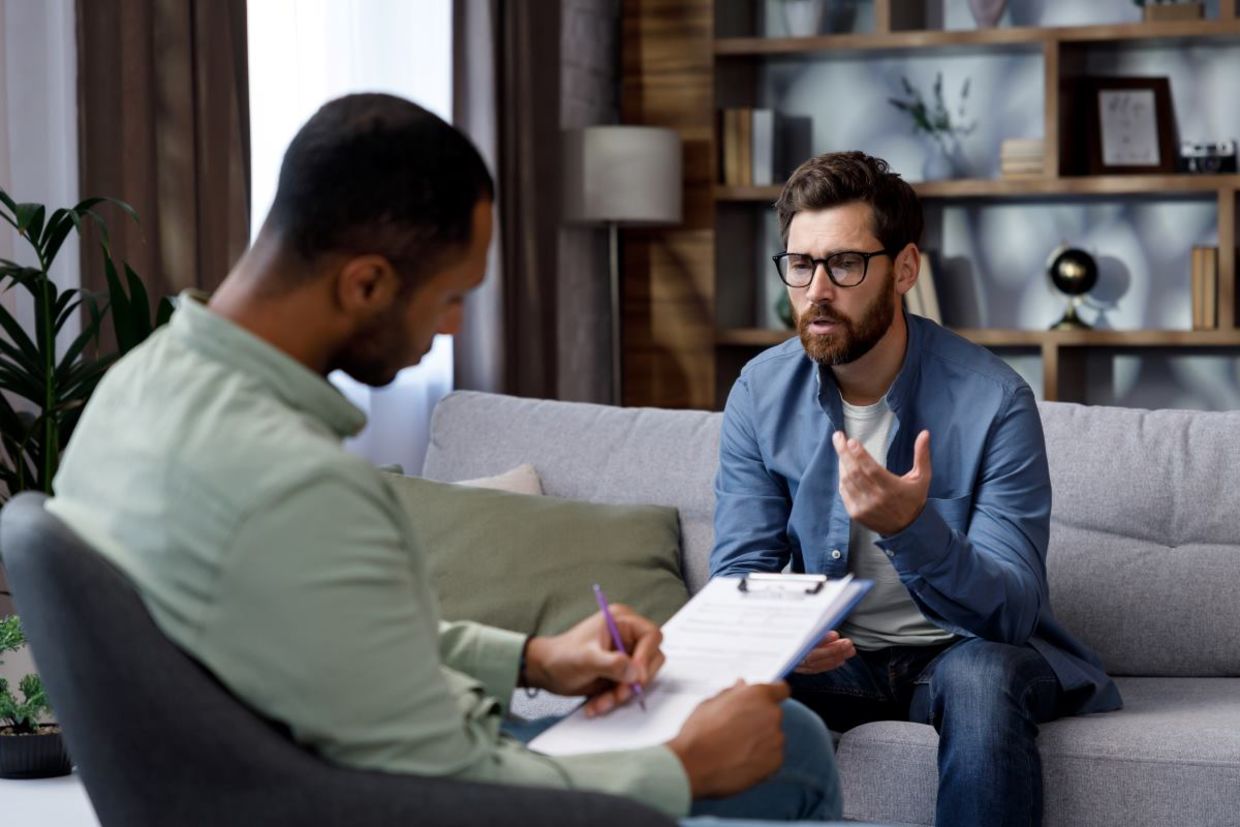
Therapy can and should be transformative – not just about helping people make needed behavioral and mindset changes, but also about self-actualization and meeting one’s goals in life.
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a subset of cognitive behavioral therapy that has successfully been employed to treat borderline personality disorder since the 1970s,according to the Cleveland Clinic. Now, therapists are exploring how DBT techniques can help people with a wide range of mental health conditions to alleviate their symptoms and achieve acceptance and self-actualization.
What is DBT
DBT is a type of psychotherapy, or talk therapy, developed by American psychologist Dr. Marsha Linehand, in the 1970s to treat people with borderline personality disorder and those experiencing intense emotions.
DBT is similar to cognitive behavioral therapy, a talk therapy that tries to help people understand how feelings and actions are linked. The therapy specifically focuses on helping participants accept their reality and validate their feelings and actions, while also working to change unhealthy or harmful behaviors.
According to verywell mind, DBT rests on six principles. The first is acceptance and change. DBT encourages patients to accept what they can’t change and work to change what they can.
The second and third principles are behavioral and cognitive and seeks to replace destructive behaviors with healthy behaviors and destructive thought patterns with healthy ones. Another principle is collaboration. This therapy requires participants to work closely with a team of practitioners involved in their treatment.
DBT also focuses on helping individuals learn new skills to regulate their emotions and behaviors. Lastly, the therapy relies on patients being supported in developing strengths and meeting goals.
How does it work?
DBT sessions will typically take place as one of four formats: pre-assessment (intake, goal setting, and determining if this type of therapy will meet the patient’s needs), individual therapy sessions, group sessions, and telephone crisis coaching.
Utilizing DBT to treat borderline personality disorder is usually done in four stages The first stage is emergency intervention – stopping self-destructive and suicidal behaviors. The second stage focused on identifying, channeling, and changing negative emotions and behaviors. During the third stage, individuals work on improving their interpersonal relationships and the last stage relates to self-actualization, pursuing goals, and building stronger relationships with others.
Common practices
Although DBT incorporates a number of cognitive behavioral therapy techniques, some common practices include: core mindfulness, distress tolerance, interpersonal, effectiveness and emotional regulation..
Core mindfulness means developing the ability to live in the moment both physically (being in tune with what the body is sensing around it using the five senses) and emotionally (developing awareness of one’s thoughts and feelings in a given situation). Mindfulness can help people to stay calm, cope with stress, and to avoid a feedback loop of negative thoughts.
Distress tolerance refers to developing a toolkit of skills to use in a crisis. These skills might involve the ability to self-soothe or to distract oneself. Interpersonal Effectiveness means learning to build healthy and positive relationships. It includes setting limits, communicating, and dealing with difficult people. Emotion Regulation relates naming and identifying feelings. It also involves shifting from negative to positive emotions and thought patterns.
Is DBT effective?
Since DBT was developed to treat borderline personality disorder, the bulk of research has focused on its effectiveness for individuals with thedisorder. Research shows that DBT is an effective treatment for the disorder; one study even found that after a year of DBT treatment for people with borderline personality disorder, 75 percent of participants no longer met the criteria for a borderline personality disorder diagnosis.
DBT can, however, be applied to treat a range of conditions, including ADHD, bipolar disorders, eating disorders, anxiety, depression, OCD, PTSD, substance abuse, and other related conditions. An Initial clinical trial found that it may be effective in treating children with disruptive mood dysregulation disorder.
If you are looking for a DBT therapist, the Cleveland Clinic recommends finding one who is licensed and familiar with treating your specific needs or diagnosis. Ask your potential therapist about their training, whether they provide comprehensive DBT, and how much time the therapy will take.
DBT isn’t a quick fix — it typically takes six months to a year — but its results can be transformative. By balancing acceptance with actionable change, DBT equips people with the skills to validate their own feelings while embracing future possibilities.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE:
This Mobile Game Helps Your Mental Wellness
This Evidence-Based Therapy can Help with Decision Making
Gen Z Balances Mental Wellness and Ambition to Drive Personal Growth